NIHR and Medidata: Knowledge, Expertise, and Collaboration Lead to Improved Clinical Trial Budgeting

Clinical Trial Budgeting Challenges
Clinical trial budgeting is challenging for several reasons. Different therapeutic areas and indications have their own unique types of trial structure and require different patient procedures. The fact that protocols are rarely the same and lack of expertise in each therapeutic area can cause issues downstream when budget builders do not fully understand the needs for a specific protocol. Additionally, many specific country regulations and inconsistent processes across regions can easily lead to a lack of transparency between sponsors, CROs, and sites.
It’s imperative to know country comparisons in order to make sure the right choices are being made when looking at which countries and sites to run a study. A lack of clinical trial financial management expertise can lead to delays that impact costs and timelines, which ultimately impacts patients. The below chart illustrates the variation in cost per site visit from country to country. Using the US as the baseline (as the most expensive), site visits in Spain cost half of the cost in the US and a third in China.
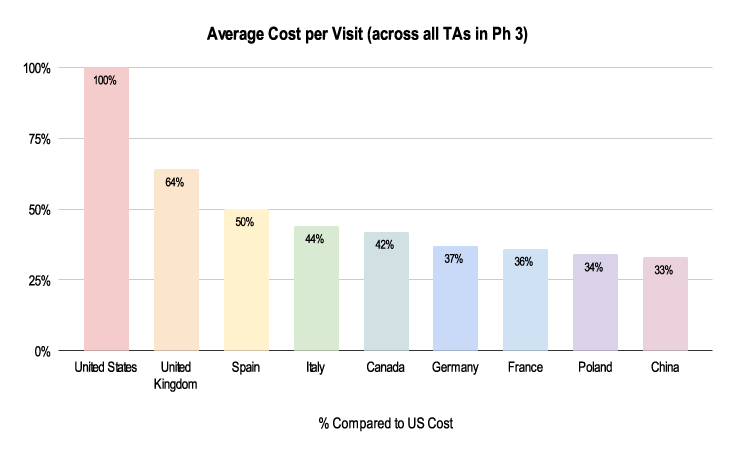 Figure 1: 2019-2021 Grants Manager Picas Database - Average Cost Per Visit, All therapeutic areas, Phase III in US Dollar.
Figure 1: 2019-2021 Grants Manager Picas Database - Average Cost Per Visit, All therapeutic areas, Phase III in US Dollar.
How Medidata and the NIHR are Addressing Clinical Trial Budgeting Challenges
Before creating the trial budget, it's important to review the entire trial protocol and not just the schedule of assessments. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of all procedures and non-procedures involved in the trial. It’s also critical to know and understand the main cost drivers, such as specific country regulations that could impact price and looking at fair market value to evaluate if you’re paying too high or too low.
Medidata
Medidata is aware of these challenges and provides solutions and applications that can alleviate them. Medidata's Rave Grants Manager can help study teams build detailed and high-level forecast budgets, allowing a better understanding of the industry benchmarks. Medidata's solution incorporates data from more than 200 countries, bringing value to the investigator grant-building process in all countries, including those countries with minimal clinical trial budget experience. Medidata subject matter expert teams specialize in clinical trial financial management (CTFM). To ensure the solution’s evolution and increase process awareness, the team spearheads collaborative innovation labs with CTFM client experts. These innovation labs include two tracks—budgeting and payments—which foster a synergetic environment to learn best practices and make sure that clients’ needs and visions lead to growth and innovation of tools like this.
The NIHR
Beyond funding and supporting clinical research, the NIHR developed the interactive costing template (iCT), which provides a framework for transparent cost display and calculation to support local site budget negotiations when planning trials. Through many of the NIHR’s networks and advisory boards, they are driving important conversations about challenges within clinical trials to fundamentally improve research and bring new treatments to market faster.
The NIHR Clinical Research Network (CRN) includes 30 specialty groups who coordinate and support the delivery of high-quality research by therapy areas.
Variances Between Therapeutic Areas
Similarly to country variances, therapeutic areas also have distinct and unique differences that impact budgeting. Looking at three different therapeutic areas—central nervous system (CNS), cardiovascular, and women’s health—demonstrates the vast differences that need to be accounted for. Below, we look at the nuances of each of these therapeutic areas, identified by analyzing Medidata’s unrivalled and extensive data through its Grants Manager solution. We also look at the work the NIHR are doing in each of these areas.
Central Nervous System
Due to the nuances listed below, budgeting for these trials can greatly differ. As shown above, the average cost per visit in a CNS trial is about half the cost in the UK and Germany compared to the US.
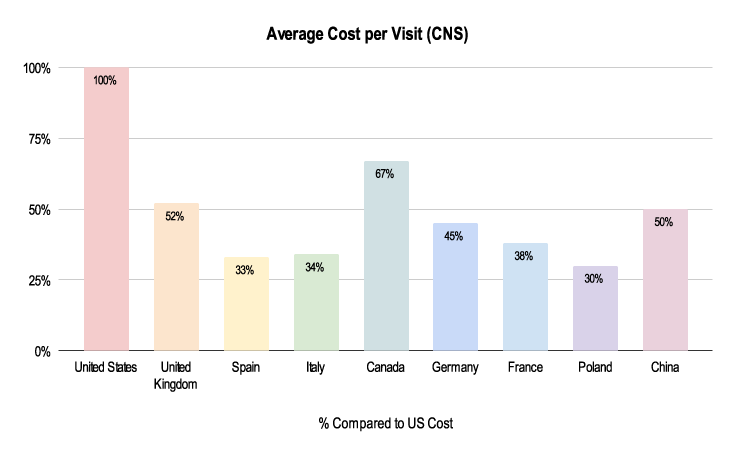 Figure 2: 2019-2021 Grants Manager Picas Database - Average Cost Per Visit, Indication: Parkinson’s Disease, Phase III in US Dollar.
Figure 2: 2019-2021 Grants Manager Picas Database - Average Cost Per Visit, Indication: Parkinson’s Disease, Phase III in US Dollar.
CNS nuances:
- It can be difficult to recruit CNS patients due to the drug washout period (the length of time that someone enrolled in a trial must not receive any treatment before receiving the trial's experimental therapy)
- These diseases are difficult to work with, so it can be hard to find neurologists willing to do these studies
- Different levels of conditions (like Parkinson’s where the degree of condition varies greatly)
- There are different rating scales to determine the disease severity—and the rater needs to been trained which has to be taken into account
- Cost Per Patient (CPP) increases, and self-administered rating scales still need to be assessed by the physician
- Alzheimer’s disease will include costs for caregivers (e.g. travel reimbursement for the carer)
Launched in March 2021, COVID-19 Clinical Neuroscience Study (COVID-CNS) is a collaboration between experts in neuroscience and psychiatry at the University of Liverpool and King’s College London, under the NIHR BioResource umbrella, to investigate the neurological and neuropsychiatric effects of COVID-19 and develop strategies to prevent and treat them. In its first year, collaborating with 17 institutions across the country, COVID-CNS has already recruited over 500 patients.
Cardiovascular
 Figure 3: 2019-2021 Grants Manager Picas Database - Average Cost Per Visit, Indication: Heart Attack, Phase III in US Dollar.
Figure 3: 2019-2021 Grants Manager Picas Database - Average Cost Per Visit, Indication: Heart Attack, Phase III in US Dollar.
Due to the nuances listed below, budgeting for these trials can largely differ. As shown above, the average cost per visit in a cardiovascular trial is about half the cost in the UK compared to the US and a fourth of the cost in Poland and China.
Cardiovascular nuances:
- There is quite a difference in costs comparing invasive vs. non-invasive indications with cardiovascular clinical trials
- Invasive indications include the need for stents and heart catheters and non-invasive indications include low or high blood pressure
- Inpatient/outpatient days (amount of days staying in hospital vs. not)
- This can massively impact study costs with overnight stays
- There will be a difference in what is covered by standard of care
- Surgery can be a huge additional cost if not covered
- More safety labs (more regular checks and assessments)
- For example, electrocardiogram (ECG) and echocardiogram (ECHO) tests
- Recruiting difficulties
- For example, hard to predict when a patient will present with a heart attack due to uncertain time windows and difficulty getting patient consent
The NIHR-British Heart Foundation Cardiovascular Partnership provides a platform for collaboration between researchers funded by NIHR and the British Heart Foundation. The ultimate goal of this academic-led initiative is to catalyze progress in cardiovascular research and translate scientific discoveries into benefits for people affected by heart and circulatory diseases.
Women’s Health
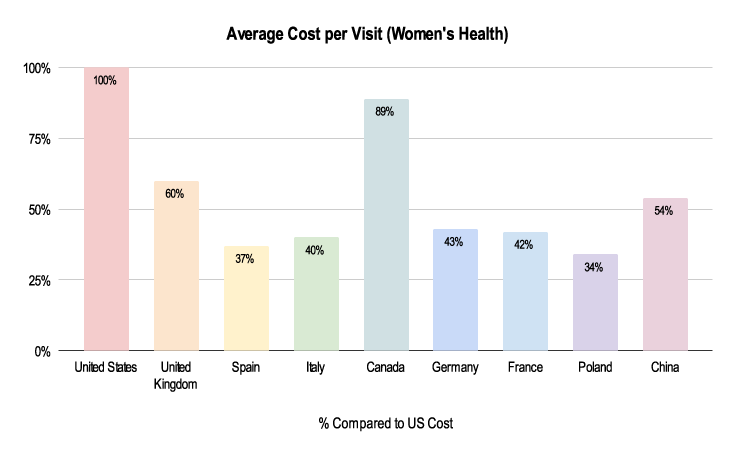 Figure 4: 2019-2021 Grants Manager Picas Database - Average Cost Per Visit, Indication: Endometriosis, Phase III in US Dollar.
Figure 4: 2019-2021 Grants Manager Picas Database - Average Cost Per Visit, Indication: Endometriosis, Phase III in US Dollar.
Due to the nuances listed below, costs for these clinical trials can be very different. As shown above, the average cost per visit in a Women’s Health trial is about half the cost in China compared to the US and about a third in Poland.
Women’s Health nuances:
- Certain indications might require special procedures that can be expensive
- For example, bone mineral density (BMD) measurements or Alkaline Hematin Method, involving chemically measuring the blood content of used sanitary products, to determine monoclonal B lymphocytosis (MBL)
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria can be very specific for gynaecology studies
- It can be hard to recruit for endometriosis studies due to lack of diagnosis (it takes, on average, ten years to receive a proper diagnosis)
- Lengthy questionnaires and electronic patient diaries (about quality of life)
- Translation, validation, compliance, and collection of diary data moving from paper to electronic
- Washout period and follow-up pill studies
- Patients might be reluctant to join a study, as well as not return for follow-ups as no clear personal benefit
Reproductive health is one of the largest recruiting specialties in the NIHR CRN Portfolio of studies, covering the full range of clinical subspecialties in women’s health. The NIHR are able to engage with approximately 700,000 women giving birth each year in the UK, as well as the many others attending gynaecology clinics and women’s health care services throughout the NHS. The portfolio covers research council, government, charity, and industry-sponsored studies.
An Ever-Evolving Future
Clinical trials are continuing to evolve with the main objective of getting new drugs and treatments to the patients that need them. Whether it’s a small rare disease study with a few hundred patients or a global COVID study recruiting tens of thousands of patients, one thing is certain: research teams, sponsors, and CROs need to do the appropriate research before starting a clinical trial to understand the budgeting and costing restraints, limitations, and potential unseen challenges.
The expertise of Medidata and the NIHR, as well as their ongoing collaboration and initiatives, are helping to address and limit these challenges to shape a truly transparent and collaborative industry between sponsors, CROs, and sites.
Click here To learn more about Medidata’s clinical trial financial management tools and solutions. To learn more about the NIHR, visit here.
Explore Related Articles
Contact Us

